Understanding Place Noise Levels: How They Affect Your Environment and Well-Being
Noise pollution is often overlooked, but it significantly impacts our daily lives. Whether it’s the sound of traffic, construction work, or nearby events, noise levels can influence your health, productivity, and overall well-being. In this article, we’ll explore the different aspects of place noise levels, their effects, and ways to manage them for a better living environment.
1. What Are Place Noise Levels?
Place noise levels refer to the amount of sound or noise in a specific area. These levels are typically measured in decibels (dB), which quantify the intensity of sound. Noise levels vary depending on the environment—whether it’s an urban area, a quiet park, or a busy restaurant.
Noise can come from various sources, including traffic, machinery, social events, or natural elements like wind or animals. High noise levels are often linked to urbanization and industrialization, while quieter spaces can be found in rural areas or designated quiet zones. Understanding place noise levels is essential for improving both your comfort and health.
2. How are Noise Levels Measured?
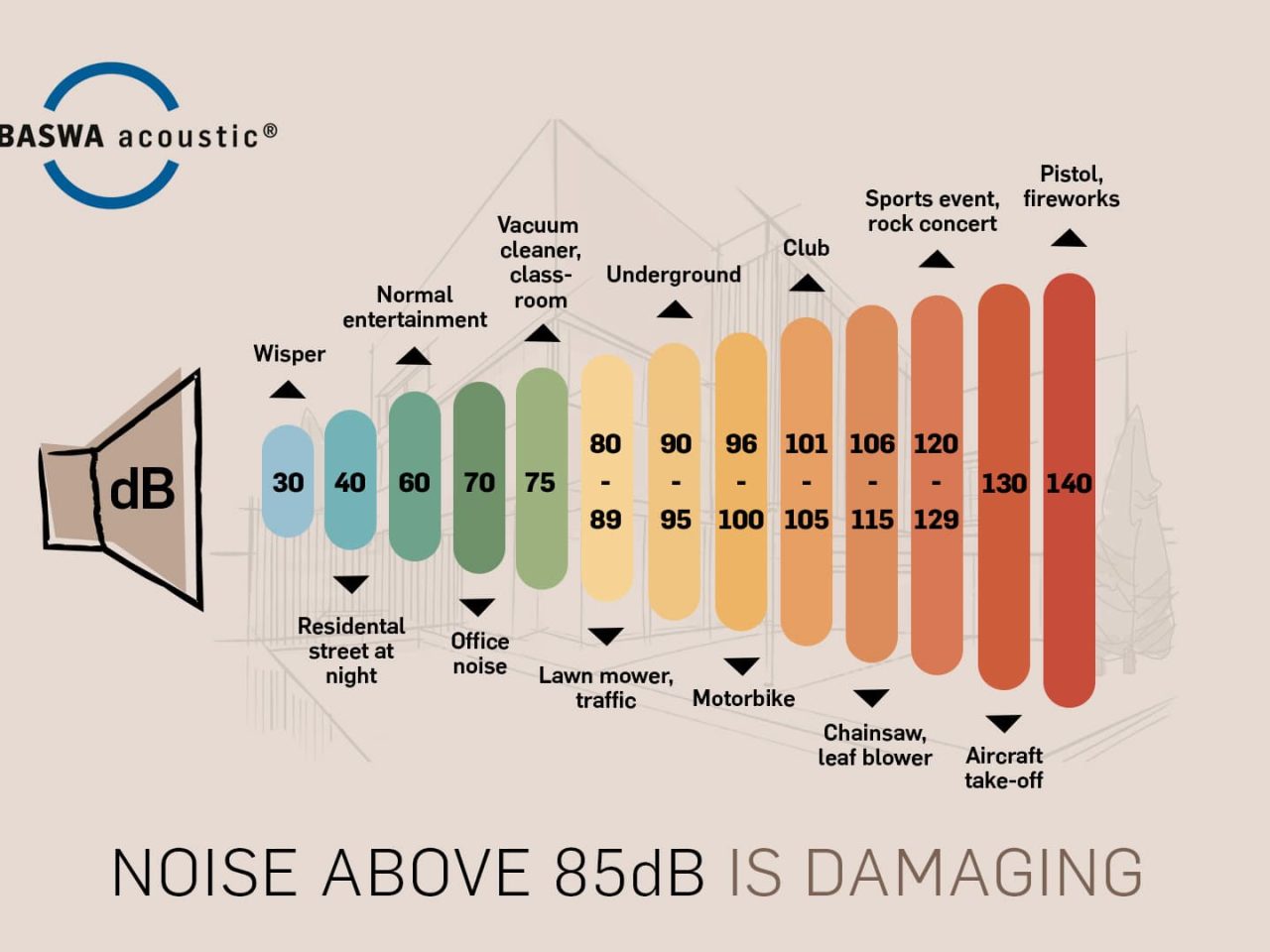
Noise levels are typically measured in decibels (dB), with different thresholds indicating varying levels of sound intensity. Here’s a general guide to common noise levels:
-
30 dB: Whispering or a quiet rural area
-
50-60 dB: Normal conversation
-
70-85 dB: Busy street or traffic
-
90 dB and above: Industrial machinery, loud music
-
120 dB: Threshold of pain (e.g., chainsaws, jet engines)
The higher the dB, the more intrusive and potentially harmful the noise becomes. For instance, prolonged exposure to noise levels above 85 dB can lead to hearing damage over time.
Measuring Noise with Tools
To accurately measure noise levels, professionals use tools like sound level meters and noise dosimeters. These devices record decibel readings, which help assess environmental noise, workplace sound, and potential hazards.
For a more accurate understanding of place noise levels in your area, check our Noise Measurement Guide for tips on choosing the right tools.

3. Sources of Noise Pollution
Noise pollution can come from many sources, each affecting different areas of life. Here are some of the most common contributors to high place noise levels:
a. Traffic and Transportation
One of the primary sources of noise pollution in urban areas is traffic. The sound of cars, buses, and trains constantly moving can elevate noise levels, especially in busy streets and intersections. In major cities, noise from transportation is often above the safe threshold, causing disturbances in residential and commercial areas.
-
Pro Tip: Consider investing in soundproofing solutions for homes or offices located near busy roads.
b. Construction and Industrial Activities
Construction sites and factories produce high levels of noise from machinery and equipment. The noise can be particularly overwhelming during work hours, affecting the productivity of nearby residents and workers. These sources can create continuous and disruptive noise that lasts for hours.
-
Pro Tip: Governments often impose regulations on noise levels in construction zones to minimize the impact on the surrounding environment.
c. Social Events and Public Gatherings
Festivals, concerts, or sporting events can contribute to high place noise levels. While these events are often temporary, they can cause significant noise pollution if they occur frequently or late at night. Noise from these activities can travel long distances, affecting neighborhoods.
-
Pro Tip: Local authorities often regulate the hours during which loud events can occur. Checking for local noise ordinances can help you avoid noise disturbances.
d. Natural Sounds
While not typically associated with pollution, natural sounds like wind, rain, and animals can also affect noise levels in specific areas. In rural or suburban areas, these sounds may not be as intrusive, but in urban parks or near forests, they can provide a different experience of noise levels.
For a detailed breakdown of noise sources and how they affect different areas, explore our Comprehensive Guide to Noise Pollution.
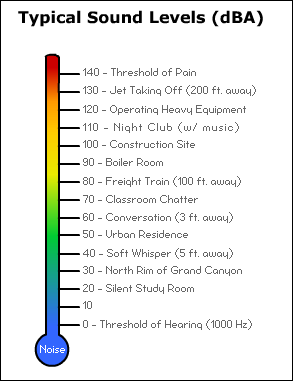
4. The Impact of Noise Levels on Health
High noise levels in your environment don’t just affect your ears—they can also have significant effects on your overall health and well-being. Chronic exposure to excessive noise can lead to a range of physical and psychological issues.
a. Hearing Loss
One of the most direct consequences of prolonged exposure to loud noise is hearing loss. Noise levels above 85 dB can damage the hair cells in the inner ear, leading to permanent hearing impairment. Individuals working in loud environments like factories or construction sites are at greater risk for hearing damage.
-
Pro Tip: Use ear protection (e.g., earplugs or earmuffs) when exposed to loud environments.
b. Increased Stress Levels
Constant exposure to high noise levels can cause elevated stress levels. The body reacts to noise by releasing stress hormones, which can lead to feelings of anxiety and fatigue. Over time, this can contribute to cardiovascular problems, including high blood pressure and an increased risk of heart disease.
-
Pro Tip: Reducing noise exposure and practicing relaxation techniques can help manage stress effectively.
c. Sleep Disruption
High noise levels during the night can interfere with your sleep cycle, leading to poor rest and overall fatigue. Noise from traffic, construction, or neighbors can disrupt your sleep, resulting in decreased productivity and poor mental health.
-
Pro Tip: Soundproofing your bedroom or using white noise machines can help mitigate the effects of nighttime noise.
d. Reduced Cognitive Function
Exposure to loud noise can also impair cognitive performance, particularly in children and the elderly. Studies have shown that noise pollution can reduce attention span, memory, and learning abilities, leading to decreased productivity in both work and academic settings.
For more information on the effects of noise on health, visit our Health and Noise Pollution Page.
5. Ways to Manage and Reduce Noise Pollution
While completely eliminating noise pollution may not always be possible, there are several strategies to manage and reduce place noise levels in both residential and commercial environments.
a. Soundproofing
Soundproofing is one of the most effective ways to reduce noise in your space. It involves using materials like acoustic foam, soundproof windows, and heavy curtains to block out unwanted sound. For businesses located in noisy areas, soundproofing offices or workspaces can enhance employee productivity and overall satisfaction.
-
Pro Tip: Install soundproof doors and windows to create a quiet environment, even in the noisiest locations.
b. Landscaping and Barriers
In some cases, landscaping can help reduce noise levels. Tall trees, shrubs, and sound barriers can absorb and block external noise from roads or other sources. In commercial spaces, installing acoustic barriers along the property line can significantly reduce noise pollution.
-
Pro Tip: Use plants with dense foliage to absorb sound waves effectively.
c. Noise Regulations
Governments around the world have introduced noise regulations to manage pollution levels. These regulations set limits on the amount of noise allowed in certain zones, particularly residential or quiet areas. Businesses and construction sites are often required to operate within these guidelines to minimize the impact on surrounding communities.
-
Pro Tip: Familiarize yourself with local noise ordinances and ensure your business complies with them to avoid penalties.
For more about noise management and legal regulations, refer to our Noise Control Resource.
6. Conclusion: Managing Noise for a Healthier Environment
Place noise levels play a significant role in shaping our daily experiences, influencing our health, and determining the overall quality of life. By understanding the sources and impacts of noise, individuals and businesses can take steps to minimize exposure and create more peaceful environments.
Whether it’s soundproofing your home, using noise barriers in commercial spaces, or following noise regulations, effective management of noise pollution contributes to both physical and mental well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is considered a dangerous noise level?
Noise levels above 85 dB are considered dangerous and can cause hearing damage if exposure is prolonged.
2. How can I reduce noise in my apartment?
You can reduce noise by using soundproofing materials, installing heavy curtains, and placing rugs on floors to absorb sound.
3. Is there any law regulating noise levels?
Yes, most cities have noise ordinances that regulate the maximum allowable noise levels in residential and commercial zones.
4. Can noise affect my productivity?
Yes, high noise levels can impair concentration and reduce cognitive performance, affecting overall productivity.
For further information on noise pollution management, check out our Noise Reduction Tips.
By taking the proper steps to manage place noise levels, you can create a more peaceful, productive, and healthy environment for yourself and those around you.
